A migraine is a complex neurologic disorder characterized by significant disability due to pain and symptoms associated with attacks. According to the World Health Organization, migraines are the eighth most disabling disease worldwide, the most burdensome neurologic disease, and responsible for 5.6% of years lost to disability. The disability includes missed school or work, inability to perform household chores, and missed time with family and friends. Migraines are most common between the ages of 18 and 44, with higher rates in females, and a peak in prevalence in both men and women in their 40s. 18% of American women, 6% of men, and 10% of children experience migraines. Migraines tend to run in families, and about 90% of migraine sufferers have a family history of them.
There are several types of migraines which include migraine without aura, migraine with aura, hemiplegic migraine, etc. Migraine without aura is the most common type, defined as at least 5 attacks lasting 4 to 72 hours, with at least two defining characteristics (unilateral, pulsating, moderate or severe pain, aggravated or caused by deliberate avoidance of physical activity), at least one related symptom (nausea, vomiting, photophobia-sensitivity to light or phonophobia-sensitivity to sound). Around 36% of migraines have an associated aura. Migraine with aura describes a migraine in which the person experiences some type of sensation associated with the onset of a migraine. The common aura symptoms include blind spots in the field of eyesight, colored spots, sparkles or stars, flashing lights before the eyes, tunnel vision, zig zag lines or temporary blindness.
phonophobia-sensitivity to sound). Around 36% of migraines have an associated aura. Migraine with aura describes a migraine in which the person experiences some type of sensation associated with the onset of a migraine. The common aura symptoms include blind spots in the field of eyesight, colored spots, sparkles or stars, flashing lights before the eyes, tunnel vision, zig zag lines or temporary blindness.
Four main phases have been described to characterize the progression of a migraine: premonitory phase, aura phase, headache phase, and postdrome phase. In the premonitory phase, functional magnetic resonance imaging study shows evidence of hypothalamic, thalamic, and cortical activation during this phase which correlates with yawning, polyuria, irritability, photophobia, mood changes, difficulty concentrating, and neck pain. The aura phase involves disruptive changes in the sensorium in which visual auras are the most common type. The pathophysiology of migraine in the aura phase is described by the concept of cortical spreading depolarization, in which vasoactive substances, such as nitric oxide, are released, resulting in increased cerebral blood flow. The headache phase is driven by pain perception communicated from peripheral afferents to central control centers for pain, including cortical, vascular, and autonomic locations which make up the trigeminocervical complex. The postdrome phase is the resolution of the migraine driven by vasoconstriction and reduced cerebral blood flow that often presents with symptoms such as fatigue, difficulty concentrating, nausea, and irritability.
The induction of migraine is related to factors such as emotion, body, diet, and environment. Emotional factors include stress, anxiety, tension, shock, depression, and excitement. Physical factors include fatigue, poor sleep quality, shift work, poor posture, shoulder and neck tension, and strenuous exercise beyond daily capacity. Dietary factors include irregular diet, dehydration, drinking alcohol, intake of caffeine, certain cheeses, chocolate, foods containing tyramine, including bacon, yeast extracts, pickled herring, smoked fish, etc. It is recommended to avoid freezing or refrigerating foods that may cause tyramine content to rise. Environmental factors include bright lights, flashing screens, smoking, loud noises, environmental humidity or temperature changes, and strong odors.
In traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), a migraine is caused by exogenous wind-cold, wind-heat, wind-phlegm invasion, or endogenous stagnation of Liver qi, Liver fire, hyperactivity of Liver-yang or Liver-blood deficiency, leading to obstruction or malnutrition of the Liver or Gallbladder meridians on the head. In TCM, many techniques can be used to relieve migraine headache effectively, which include acupuncture, electroacupuncture, cupping, gua sha, etc. Acupoints in the Liver meridian such as Liver 2, Liver 3 and Gall bladder meridian such as GB7, GB8, and GB40 are used to treat migraine. Meanwhile, certain Chinese herbal medicines such as Yan Hu Suo Zhi Tong Pian (Yan Hu Suo Pain Relief Tablet) is widely used for migraine. In addition, massage, meditation, and Qigong can also relieve migraine headaches by reducing stress level, relieving head and neck tension and balancing yin and yang.


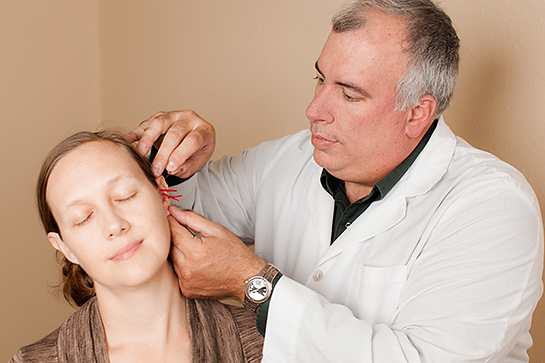-resized-600.jpg?width=224&height=149&name=clinic_lac_(6)-resized-600.jpg)

.jpg?width=200&height=150&name=herbs_(7).jpg) The most commonly prescribed Chinese herbal formulas for stress are xiao yao wan (also known as “Free and Easy Wanderer”), gan mai da zao tang, chai hu shu gan san, yi guan jian, yue ju wan, and gui pi tang. To find out the right herbs for you,
The most commonly prescribed Chinese herbal formulas for stress are xiao yao wan (also known as “Free and Easy Wanderer”), gan mai da zao tang, chai hu shu gan san, yi guan jian, yue ju wan, and gui pi tang. To find out the right herbs for you, 










 h their eyes closed, hands resting upward — thumb and index finger touching — while my younger siblings crawl on their backs and shoulders. My older two brothers and I sit nearby, holding our own meditation poses, bored, rolling our eyes and counting the minutes until this ritual will end.
h their eyes closed, hands resting upward — thumb and index finger touching — while my younger siblings crawl on their backs and shoulders. My older two brothers and I sit nearby, holding our own meditation poses, bored, rolling our eyes and counting the minutes until this ritual will end. Renée Peterson Trudeau is president of Career Strategists and the author of the new book Nurturing the Soul of Your Family. Thousands of women in ten countries are participating in Personal Renewal Groups based on her first book, the award-winning The Mother’s Guide to Self-Renewal. Visit her online at
Renée Peterson Trudeau is president of Career Strategists and the author of the new book Nurturing the Soul of Your Family. Thousands of women in ten countries are participating in Personal Renewal Groups based on her first book, the award-winning The Mother’s Guide to Self-Renewal. Visit her online at 


